Revolutionizing Agriculture: The Promise of Nitroplasts
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Nitroplasts
In a significant breakthrough for agricultural science, researchers have recently identified nitroplasts — an innovative type of plant organelle that could change the landscape of food production. This remarkable finding not only aims to boost crop productivity but also presents a sustainable alternative to conventional nitrogen fertilizers, which often have detrimental environmental effects. “Revolutionizing Agriculture: The Promise of Nitroplasts” delves into this fascinating development and its potential impact on farming practices.
Nitroplasts Explained
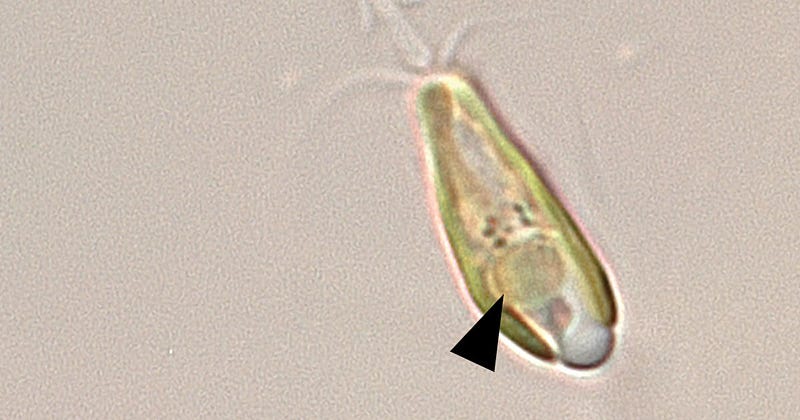
Nitroplasts are unique structures within plant cells that possess the remarkable ability to capture atmospheric nitrogen directly. This capability, similar to that of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, enables plants to transform atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which they utilize to create vital amino acids and other essential nitrogen compounds necessary for their growth.

The Science of Nitroplasts
- Biological Nitrogen Fixation: Unlike conventional plants that depend on soil-based nitrogen supplied by fertilizers, plants endowed with nitroplasts can directly access nitrogen from the atmosphere, potentially reducing or even eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Genetic Engineering: The discovery of nitroplasts was made feasible through advanced genetic and biotechnological techniques, indicating that these organelles could potentially be introduced into a diverse array of crops through genetic modification.
Impacts on Crop Production
The integration of nitroplasts into commercial farming could significantly alter agricultural methods worldwide, leading to greater efficiency and sustainability.
Enhanced Crop Yields
- Reduced Fertilizer Dependency: With the ability to fix their own nitrogen, crops that contain nitroplasts can thrive in less fertile soils and harsher climates, potentially boosting food production in previously unproductive areas.
Environmental Advantages
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The use of nitrogen fertilizers is a major contributor to nitrous oxide emissions, a powerful greenhouse gas. Reducing fertilizer application could considerably lessen the carbon footprint of agriculture.
- Improved Soil Health: Excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to soil degradation and pollution. Nitroplasts may help sustain soil health by minimizing the need for chemical fertilizers.

Challenges and Future Research Directions
Despite the exciting prospects that nitroplasts present, several challenges must be addressed before their widespread implementation:
- Concerns Regarding Genetic Modification: Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) frequently encounter public and regulatory challenges that may hinder the acceptance of crops enhanced with nitroplasts.
- Technical and Economic Obstacles: Implementing nitroplasts into various crop species will necessitate advanced biotechnological processes, which may entail significant expenses.
Conclusion: Paving the Way for Sustainable Agriculture
The identification of nitroplasts could herald a new chapter in agriculture, merging cutting-edge technology with ecological sustainability. By potentially eliminating the reliance on nitrogen fertilizers, nitroplasts promise a future where farming is more sustainable, cost-effective, and less reliant on chemical inputs.
Chapter 2: Exploring the Green Revolution to Gene Revolution
To further understand the implications of this discovery, check out the following video:
The video titled "Green Revolution to Gene Revolution in Orphan Crops" discusses the transformative potential of innovations like nitroplasts in modern agriculture. It explores the shift from traditional farming practices to advanced genetic techniques that could reshape how we approach food production.