Augmenting Humanity: The Necessity and Risks of Technology
Written on
Chapter 1: The Essential Role of AI and ML
As technology continues to evolve, the integration of AI and machine learning (ML) has transitioned from being merely advantageous to essential. These technologies not only assist in decision-making but also possess the ability to create, learn, and act autonomously. When enhanced by mechanical functions, AI can operate intelligently within the physical world.
Generative AI stands out for its capacity to produce diverse outputs, from written content to art. For instance, the platform Pencil utilizes generative AI to craft distinctive advertising materials. OpenAI's GPT-3 model exemplifies this capability; it leverages deep learning to generate text that closely mimics human writing. Its proficiency in transforming plain English into programming code is remarkable, often making it difficult to differentiate between human and AI-generated content.
Here is an example of artwork generated through AI. The models undergo training using existing artworks, enabling them to create entirely original pieces.
Chapter 2: Enhancing Learning with Technology
Advancements in technology are revolutionizing how we enhance our learning experiences. By integrating computer vision, sound analysis, and augmented reality, we can significantly improve our ability to acquire new skills. The following video illustrates a novel method for learning to play the piano.
Moreover, recent innovations allow for remote operation of tasks, as showcased in an experiment by Family Mart. Employees can now manage inventory in grocery stores from a distance using tele-operated robots.
Chapter 3: The Emergence of Human-like Robots
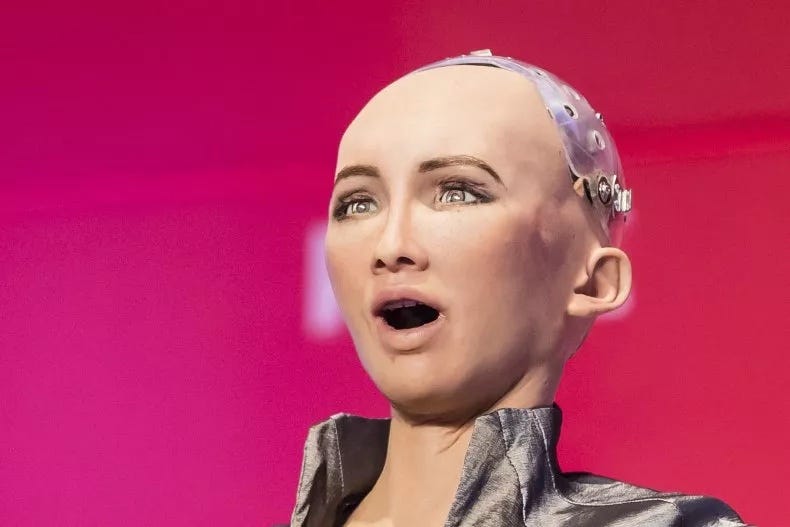
Sophia, developed by Hanson Robotics, is a notable example of a robot designed to emulate human emotions through facial expression mimicry and a semblance of self-awareness. This ambitious project raises numerous questions about the future of robotics and AI.
Sophia's ability to replicate human facial expressions involves simulating the movements of 42 facial muscles.
