A Comprehensive Overview of AI's Journey Through Time
Written on
Chapter 1: The Genesis of AI
Recently, I had a conversation with a friend who specializes in software testing. He immigrated to Canada in 2021, four years after I did. During our 24-minute chat, we shared insights about life, and I voiced my dissatisfaction with my salary. He responded, “At least you won’t be replaced by AI!”
The topic of artificial intelligence has been a hot discussion, especially during the pandemic. The emergence of technologies like 'Chat GPT' captivated tech enthusiasts, who eagerly explored its capabilities. However, the concept of AI isn't new; it traces back to the early 1950s.
The Birth of AI
The journey began with Charles Babbage's invention of the first computer, which was essentially a calculator. In 1943, the first electronic computer, known as ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), was constructed.
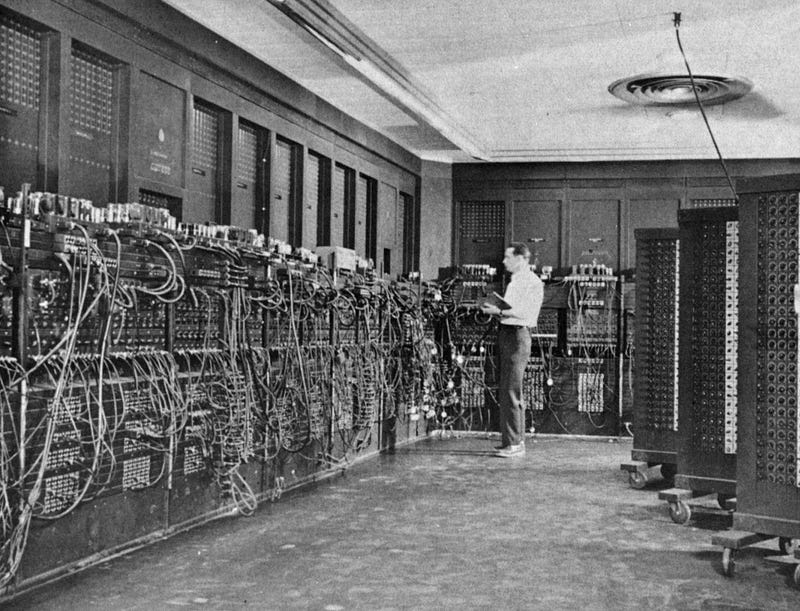
This machine was enormous, occupying an entire room, and would likely fill my entire house if it existed today. Yet, despite its size, it lacked the intelligence of the compact devices we use now.
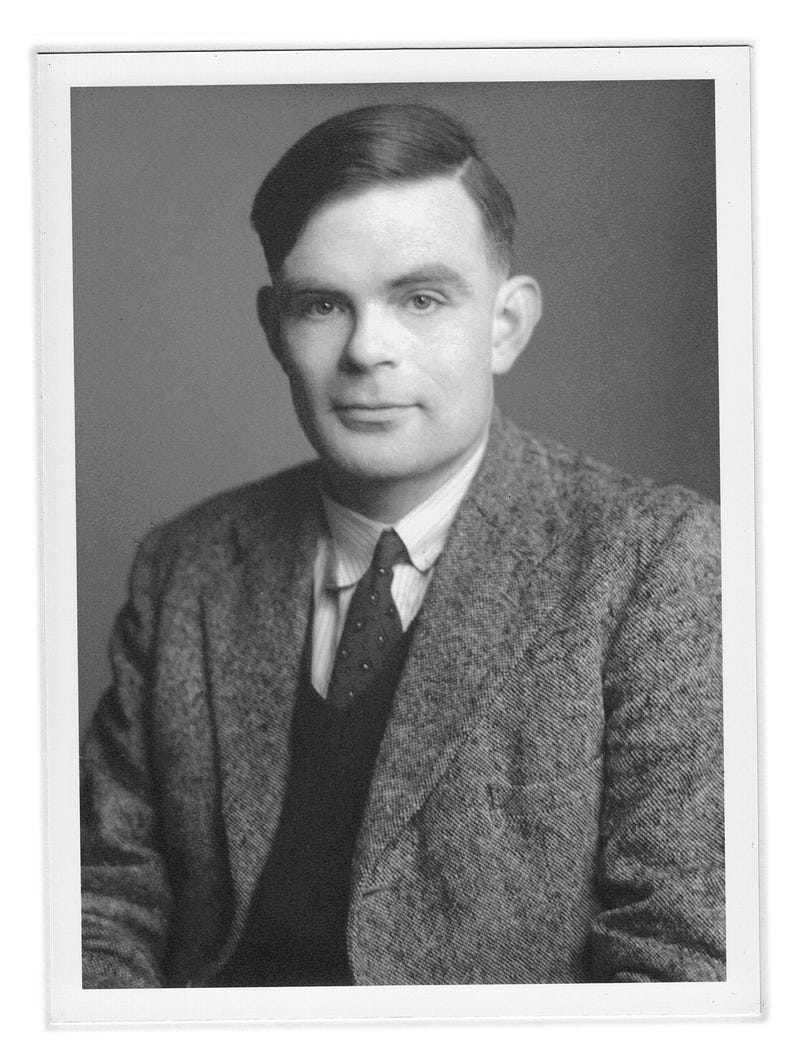

The concept of AI began to take shape in 1950 when Alan Turing pondered whether computers could utilize available information and reasoning to make decisions. Until then, computers were mere machines; Turing aimed to endow them with intelligence. His groundbreaking paper, "Computing Machinery and Intelligence," was published in 1950.

IBM's 701, a stored-program computer, utilized vacuum tubes for memory. In 1952, Arthur Lee Samuel created the first self-learning program, a checkers game, marking a significant milestone in AI development. However, the term "Artificial Intelligence" wasn't introduced until 1956, when John McCarthy used it at a workshop at Dartmouth College.
Early Development of AI
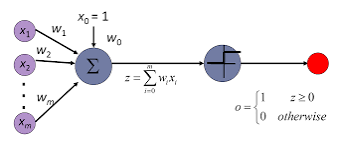
Initially, AI research focused on neural networks. In 1958, Frank Rosenblatt developed the Perceptron, an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) modeled after biological neural networks. It utilized basic logic gates with binary outputs, learning and adjusting its outputs based on the data it processed. The Perceptron algorithm served as a means for supervised learning of binary classifiers.
In 1961, the first industrial robot, Unimate, was unveiled, utilized by General Motors to handle die casings and weld automobile parts. Unimate's autonomy marked it as one of the earliest intelligent industrial robots. In 1965, Edward Feigenbaum, a Carnegie Mellon alumnus, established the first expert system, Dendral, designed to assist chemists in identifying unknown organic compounds.
History of AI Chatbots
If you're impressed by ChatGPT, you should know that older chatbots paved the way! While contemporary chatbots like ChatGPT are categorized as 'Generative AI', the earlier versions were simpler and often focused on conversational capabilities.
Joseph Weizenbaum created Eliza in 1966, the first chatbot to exhibit human-like conversation, even simulating a Rogerian psychotherapist. In 1972, Kenneth Colby developed Parry, which mimicked a patient with schizophrenia, aiming to understand and diagnose mental health issues.
The lighter side of chatbots emerged with Jabberwacky in 1988, designed by Rollo Carpenter to engage in entertaining human-like conversations. Following this, Dr. Sbaitso aimed to simplify human interaction. In 1995, A.L.I.C.E. (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity) was launched, utilizing AIML (Artificial Intelligence Markup Language). Smartchild debuted in 2001, resembling today's AI chatbots.
IBM's Watson gained fame in 2010 by competing against top players on Jeopardy.
Apple introduced Siri in 2011 with the iPhone 4S, followed by Microsoft's Cortana in April 2014. Prior to these advancements, most AI systems primarily focused on basic conversational tasks.
After a period of relative obscurity, Jasper AI emerged in 2021 as a generative copywriting tool for business owners, garnering both accolades and criticism for its potential to transform copywriting. In 2022, ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, made headlines as a sophisticated generative AI software capable of executing complex tasks, with many users employing it for their professional needs.
AI Winters — Are We Heading for Another?

As one of the most advanced technologies created by humans, AI requires significant funding for research. While various sources have provided financial support, there have been notable periods of reduced funding due to shifting interests and unrealistic expectations.
The first AI winter occurred between 1974 and 1980, characterized by limitations in AI programs that did not meet expectations. The second AI winter spanned from 1987 to 1990, during which people anticipated major advancements in AI, but the technology remained largely in its foundational stages.
Some experts speculate that ChatGPT may represent the peak of AI software, suggesting a potential decline in interest in the coming years. This could usher in a third AI winter unless innovative breakthroughs emerge. For now, we can only maximize the use of the tools currently available to us.
Sources
Harvard University
Computer History Museum
IEEE Computer Society
Stanford University
IEEE Robots Guide
IEEE Computer Society (2)